Beyond Chatbots: How the Model Context Protocol (MCP) Turns LLMs into “Action-Oriented” AI ?
Since the emergence of large language models (LLMs), we’ve witnessed their astonishing capabilities in text generation, summarization, and Q&A. However, no matter how intelligent these models are, they mostly remain at the “chatbot” stage—passively responding to queries, relying on static training data, and lacking the ability to interact with the real world.
Imagine telling an AI:“Check our CRM system for last month’s top-performing customer and automatically send them a thank-you email.” If the AI replies:“I’m sorry, I don’t have access to your CRM system or email tools,” its usefulness would be greatly diminished.
To bridge this gap between AI and real-world action, the tech community introduced a groundbreaking open standard — the Model Context Protocol (MCP). MCP effectively gives LLMs “hands and feet,” transforming them from knowledge conveyors into proactive, task-executing “AI Agents. ”
1. Two Fundamental Limitations of Traditional LLMs
Before understanding MCP’s significance, we must first recognize the two inherent weaknesses of traditional LLMs:
Limitation 1: Knowledge Boundaries and Lack of Real-Time Awareness
All LLM knowledge comes from their training data. This means:
- Outdated information: LLMs cannot know anything that happened after their training cutoff date—such as today’s stock prices, breaking news, or internal company data.
- Lack of domain-specific context: Models have no access to private enterprise data such as ERP inventory levels or CRM customer records—information not included in public training datasets.
Limitation 2: Inability to Execute External Actions
Traditional LLMs are text processors. They can generate language but cannot directly perform “input/output” actions in external systems. Tasks like clicking web buttons, editing database fields, or sending Slack messages are beyond their reach—limiting their ability to integrate into enterprise workflows.
2. MCP: Building a Bridge Between AI and the Real World
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) provides a standardized communication framework that allows LLMs to securely request up-to-date information and execute real-world actions.
Core Mechanism: Tool Invocation and Context Injection
MCP doesn’t let LLMs connect directly to the internet or databases. Instead, it introduces a structured intermediary layer:
- Definition of Capabilities:
Developers define what tools the AI can use. These tools correspond to specific APIs or scripts (e.g., “Query company database,” “Send Teams notification”). - Autonomous Decision-Making:
When a user makes a request (e.g., “Book a flight from London to Tokyo tomorrow”), the LLM determines which tools it needs according to the MCP protocol. - Standardized Request:
The LLM sends a structured request to the MCP server, specifying the tool and parameters (e.g., Tool: search_flight, Params: departure=London, destination=Tokyo, date=tomorrow). - Context Return and Action Execution:
The MCP server interacts with external systems (e.g., flight-booking APIs) and returns structured results (e.g., flight lists and prices) to the LLM. The model then uses this real-time context to generate a final response or decide the next step.
Through this process, LLMs gain real-time context and the ability to indirectly execute complex actions.
3. How MCP Elevates LLMs into Full AI Agents
MCP is the key to scaling AI Agent applications, enhancing LLM capabilities in three dimensions:
Dimension 1: From Passive Responses to Autonomous Decisions (Autonomy)
Traditionally, users had to specify every step. With MCP, AI gains planning ability:
- Example:
User: “Write an email asking IT to review a new employee’s account setup.”
With MCP: The AI autonomously breaks the task down—calls the “Query_HR_System” tool to get the employee ID, then uses the “Send_Email” tool to compose and send the message to IT. The workflow is executed end-to-end automatically.
Dimension 2: From Isolated Models to an Integrated Ecosystem (Interoperability)
As an open standard, MCP acts as a universal connector:
- Cross-system collaboration: Different LLMs (e.g., Claude, GPT, open-source models) can use the same MCP protocol to access shared enterprise systems like CRM.
- Plug-and-play extensibility: When a company adds a new internal system, it only needs an MCP-compatible interface. Any MCP-enabled AI agent can immediately use it—no retraining or code modification required.
Dimension 3: From Cloud to On-Premises Security (Security & Privacy)
For enterprises prioritizing data security, MCP offers an elegant solution:
- Local data access: MCP servers can be deployed on-premises or on employee machines, allowing AI to safely access local documents, private databases, or code repositories—without sending sensitive data to external LLM providers.
- Access control: MCP supports fine-grained permission management, ensuring AI can only use authorized tools—minimizing the risks of data leaks or unauthorized actions.
MCP Is Redefining the Practical Boundaries of AI
The emergence of MCP marks a turning point in AI development. It transforms LLMs from excellent “readers and writers” into intelligent workers that can actually “get things done.”
By granting AIs the ability to access external systems and perform actions, MCP enhances not only accuracy and real-time responsiveness but also opens new frontiers for enterprise automation, customer service, and data analysis.
Soon, we’ll move beyond chatbots and embrace a new era of collaborative, decision-making, and action-capable AI Agents.
Real-World MCP Applications by Industry
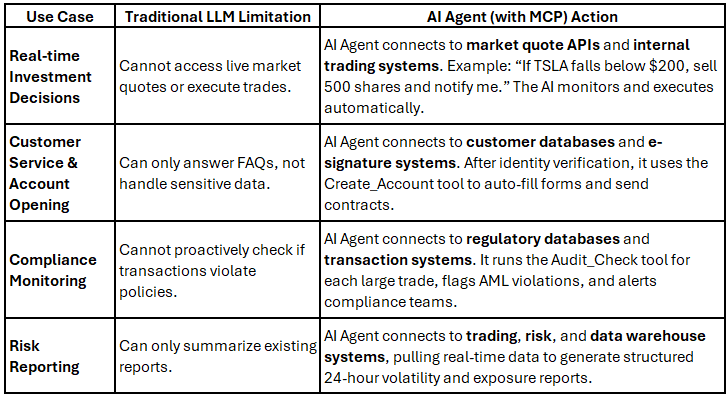
Case 1: Financial Services
The finance sector relies heavily on real-time data, regulatory compliance, and precise execution—areas where traditional LLMs fall short. MCP bridges this gap.
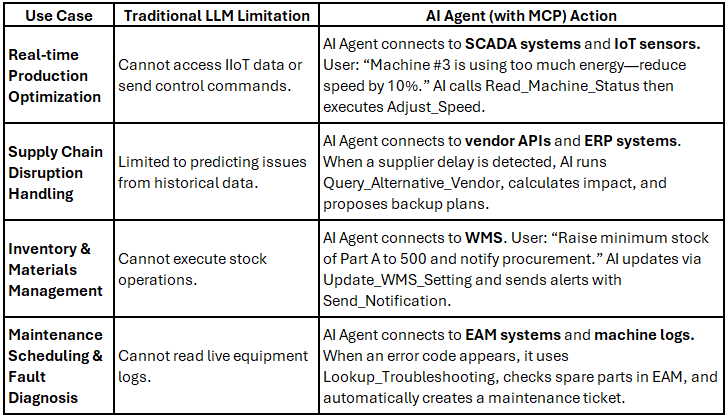
Case 2: Smart Manufacturing & Supply Chain Management
Manufacturing demands real-time control of production lines, inventory, and logistics. MCP allows AI to directly interface with Operational Technology (OT) and supply-chain software.
Conclusion
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) fuses the LLM’s semantic understanding power with enterprise-specific execution capabilities. It transforms AI from a “talker floating above data” into a true “doer” embedded in business workflows.
Whether in highly regulated, data-sensitive sectors like finance or precision-driven industries like manufacturing, MCP stands as the essential standard for the next generation of “action-capable AI applications. ”



